Opening date: 14 January 2019
Deadline for submissions: 4 March 2019 - Closed
Short Description of the C4S (Context, objectives, etc)
Needs list
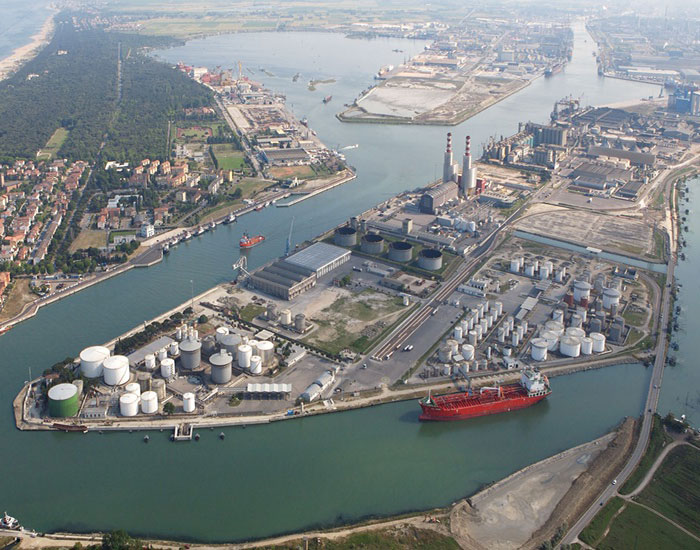
1. Supply of energy to ships during the docking phase in the port
During a 10-hour stay in the harbor, the diesel engines of a single ship can burn up to 20 tons of fuel and produce 60 tons of carbon dioxide. This is equivalent to the total emissions produced by 25 medium-sized European cars in a year. These emissions can be reduced by shore-to-ship power solutions. Driven by the recent legislative evolution in the environmental field, port authorities and shipowners in many parts of the world are trying to reduce emissions with a view to mitigating global climate impact. A valid alternative for the reduction of polluting agents is the electrification of the docks, in other words the construction of infrastructures designed to supply the electric power necessary for the operation of the auxiliaries of ships during their stay in port. However, these infrastructures require costly investments and an adequate energy distribution system, as well as the need to produce energy elsewhere.
As reported in the title of the NEED, it is therefore necessary to provide a valid technological solution for the electrification of the quays that allows overcoming technological and market barriers, evaluating the possible use of alternative energy sources for the production of electricity on site.
2. Efficient distribution of LNG
3. Energy data collection and analysis
4. Microclimate improvement
5. Facilitation to virtuous behavior
6. Spaces and/or logistics rationalization
7. Methods and solutions for an effective distribution of compressed air and refrigerant fluid to make production processes more efficient
8. Methods for the complete renovation of existing HVAC systems
According to European Commission data, the European building stock is generally inefficient, with 35% of buildings over 50 years old. These buildings, both public, residential and offices, are characterized by old and inefficient heating, ventilation and cooling systems. The extraordinary maintenance interventions necessary for the complete overhaul of these plants are burdensome in economic terms and necessarily entail a halt in production or the need to move people elsewhere.
As reported in the NEED title, it is required to present a step-by-step methodology / process leading to the replacement (partial or total) of a dated civil installation, with the aim of containing costs and optimizing technological innovations on the basis of the given context. In this context, the use of another heating source (such as pellets, wood chips, methane, LPG) should also be considered.
9. Three year payback period
10. Roofs to produce energy from the bound or dated buildings
11. Efficienct lighting/equipment management
12. Lowering peak power and Excessive reactive electricity
13. Implementing RES production
14. Zero energy mobility for tourists